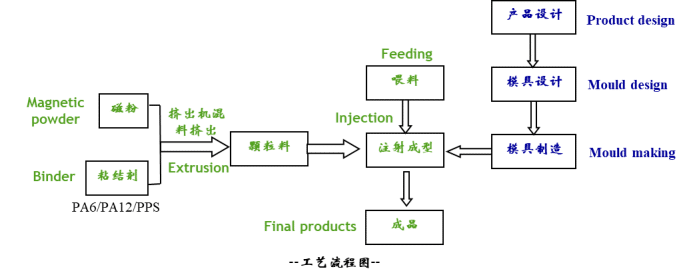
Magnetic materials are made by mixing plastic binders (such as PA6, PA12, PPS, etc.) with magnetic powder particles (such as ferrite, NdFeB, SmCo, etc.) and extruding them into granules, which can then be injection-molded using an injection molding machine.

General production process:
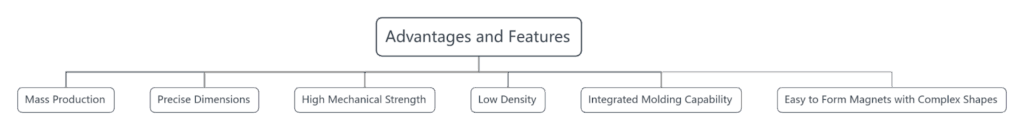
Advantages and Features:
The dimensions of injection-molded magnets correspond to the cavities of the injection mold, allowing for high dimensional accuracy. However, it should be noted that the binder used as the matrix may undergo cooling shrinkage during production, which can affect dimensional precision, so this should be carefully considered during the initial design phase.
Manufacturers of plastic-bonded magnetic powders:
| Country | Major Companies |
| China | Hangzhou Qianshi, Suzhou Beierman, Changzhou Zhongtian, etc. |
| Japan | Sumitomo (Japan), Toda (Japan), etc. |
Common Grades of Injection-Molded Magnets:
| Magnetic Powder Type | Binder | Magnetic Energy Product | Maximum Operating Temperature |
| Strontium Ferrite | PA6 | 1.45–2.41 MGOe | 150–160℃ |
| Strontium Ferrite | PA12 | 1.20–2.34 MGOe | 150℃ |
| Strontium Ferrite | PPS | 1.31–2.05 MGOe | 180℃ |
| Isotropic NdFeB | PA12 | 3.5–8.4 MGOe | 90–150℃ |
| Isotropic NdFeB | PPS | 4.4–5.9 MGOe | 150–180℃ |
| Isotropic NdFeB + Strontium Ferrite | PA12 | 2.33–6.31 MGOe | 125–150℃ |
| SmCo | PA12 | 9.5–11.0 MGOe | 150℃ |
| SmCo | PPS | 5.5–7.5 MGOe | 180℃ |
| SmFeN | PA12 | 8.5–14.4 MGOe | 150℃ |
Main Application Areas:
Automotive
Children’s Toys

3C Electronics

Home Appliances

Office Equipment

Instruments & Meters