What is a Linear Motor?
A linear motor is a device that directly converts electrical energy into linear mechanical motion without the need for any intermediate transmission mechanisms. Depending on the type of power supply, linear motors can be classified into DC linear motors and AC linear motors. They can also be categorized as iron-core linear motors or coreless linear motors, based on whether or not they contain an iron core.
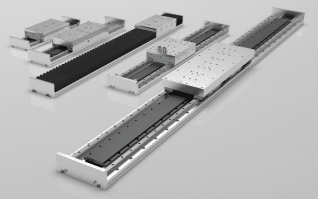
Basic Components of a Linear Motor
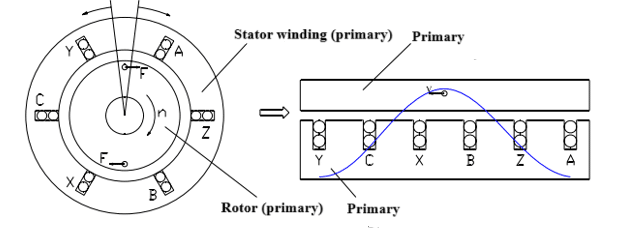
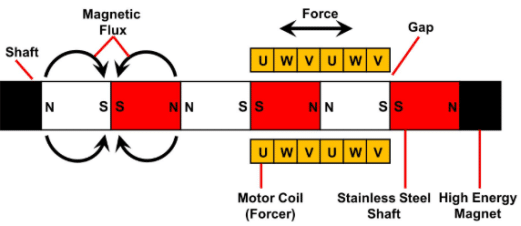
A linear motor typically consists of a stationary part (including permanent magnets) and a moving part (including coil windings). The coil winding side is generally referred to as the primary, while the permanent magnet side is called the secondary. The permanent magnets are arranged in an alternating N-S-N-S sequence, and the number of magnetic poles depends on the designed stroke length of the linear motor.
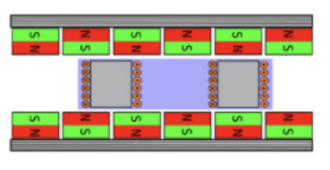
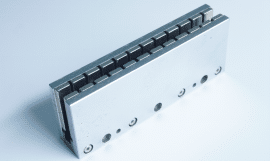
Basic Principle of a Linear Motor
In simple terms, a linear motor can be regarded as a rotary motor that has been cut along the radial direction and unfolded into a linear form. When current flows through the coil windings, the resulting electromagnetic force interacts with the magnetic field of the permanent magnets, thereby generating linear motion.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Motors
| No. | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| ① | Direct drive: eliminates transmission losses, fast response, high precision (micron level) | High cost: permanent magnet materials and control systems are expensive. |
| ② | High speed: speeds can exceed 5 m/s, far surpassing traditional ball screw systems | Thermal challenge: requires forced cooling during high-power operation. |
| ③ | Low maintenance: no contact parts (e.g., brushes), long service life | Complex control: requires high-precision sensors (e.g., linear encoders) and real-time controllers. |
| ④ | Flexibility: adaptable to long strokes and complex paths (e.g., circular tracks) | Magnetic leakage: requires shielding design to prevent interference with surrounding equipment. |
Main Application Areas of Linear Motors
| No. | Application Areas |
| ① | Transportation: maglev trains, electromagnetic launch systems |
| ② | Industrial automation: precision machine tools, laser cutting machines, laser welding machines, laser scanning, 3D printing, lithium battery assembly lines |
| ③ | Semiconductor manufacturing: lithography machines, die bonders, chip packaging, wafer dicing |
| ④ | Medical equipment: movement of MRI diagnostic tables |
| ⑤ | Daily applications: elevators, logistics, warehousing, etc. |