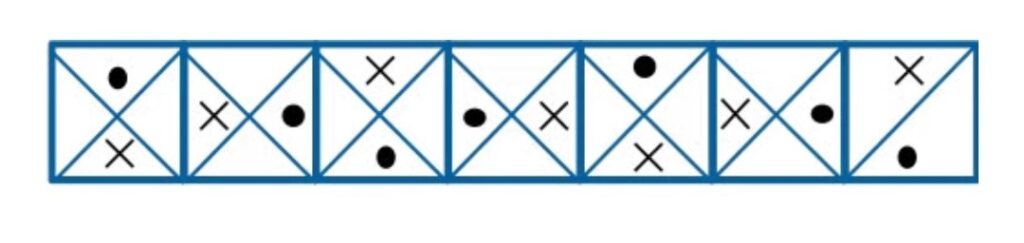
A Halbach array is a special magnet arrangement. Before exploring this structure, let’s first look at how magnetic field lines are distributed in several common types of permanent magnets.
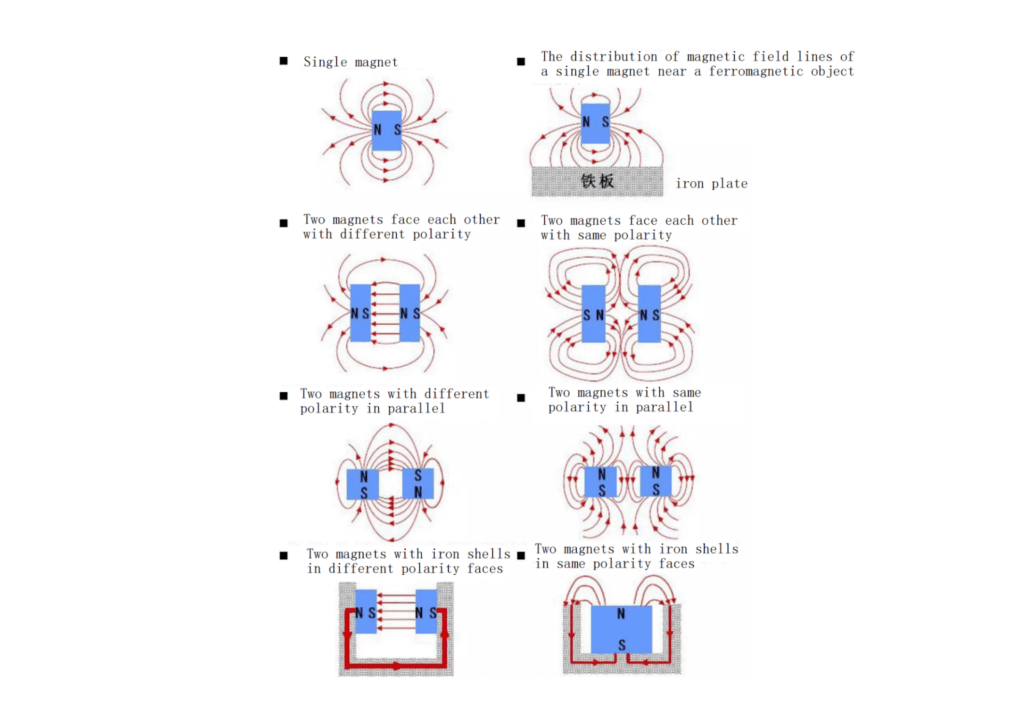
From this picture, it is not difficult to see that the orientation and arrangement of magnets directly affect the distribution of magnetic field lines—that is, the magnetic field pattern around the magnets.
The Concept of the Halbach Array
A Halbach array is a special magnetic structure. In 1979, American physicist Klaus Halbach discovered and gradually refined this unique arrangement of permanent magnets. The final result is what we now call the Halbach array, which is considered an almost ideal configuration in engineering. It uses a specific arrangement of magnetized blocks to strengthen the magnetic field on one side while weakening it on the other, with the goal of producing the strongest possible magnetic field using the fewest magnets.
This array is composed of rare-earth permanent magnets. By arranging these magnets with different magnetization directions according to a defined pattern, the magnetic field lines are concentrated on one side of the array and suppressed on the opposite side, creating a highly efficient unilateral magnetic field.
This property is extremely valuable in engineering. Because of its excellent magnetic-field distribution characteristics, the Halbach array is widely used in various industrial applications, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), magnetic levitation systems, and specialized permanent-magnet motors.
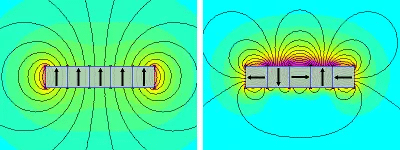
On the left is a single magnet with its north pole facing upward. From the color distribution, we can see that the magnetic field is concentrated at both the top and bottom of the magnet. On the right is a Halbach array, which produces a strong magnetic field on the top side and a much weaker field on the bottom.
Under the same overall magnet volume, the magnetic field strength on the strong side of a Halbach array is approximately √2 (about 1.4 times) stronger than that of a traditional single magnet. This enhancement is especially noticeable when the magnet thickness in the magnetization direction is between 4–16 mm.
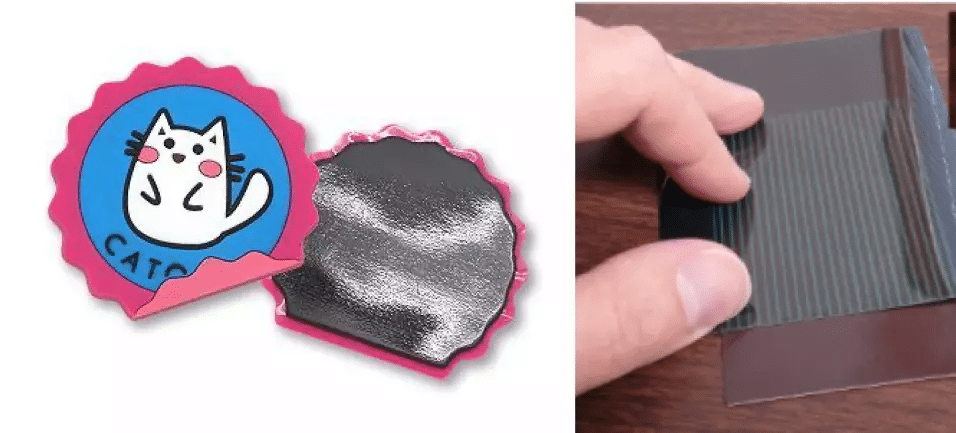
Perhaps the most familiar example of a Halbach array is the flexible refrigerator magnet. These thin and soft magnetic sheets—often printed with patterns and attached to refrigerators or car surfaces—use a simple Halbach arrangement to improve adhesion. Although they are very weak (only about 2%–3% of the strength of NdFeB magnets), they are widely used because they are inexpensive, flexible, and practical.

Forms and Applications of the Halbach Array
Linear Array
The linear type is the most fundamental form of a Halbach array. It can be viewed as a combination of radial and tangential magnetization arrangements, as shown in the figure below.
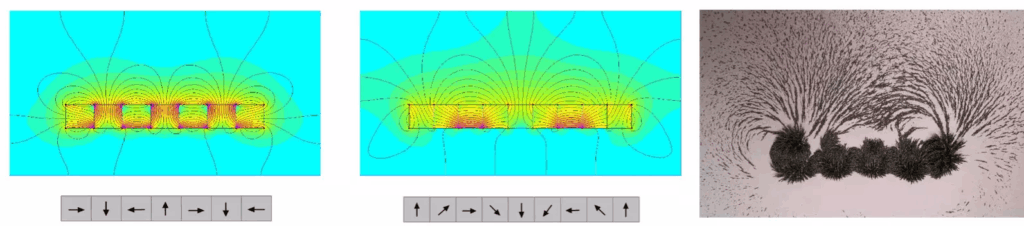
Linear Halbach Array
The linear Halbach array is mainly used in linear motors.
The levitation principle of a maglev train is that the moving magnets interact with the magnetic field generated by the induced currents in the conductors, producing both lift (levitation force) and magnetic drag. The key to improving the performance of the suspension system is to maximize the lift-to-drag ratio. This requires the onboard magnets to be lightweight, have a strong and uniform magnetic field, and ensure high reliability.
In maglev vehicles, the Halbach array is installed horizontally at the center of the vehicle body. It generates propulsion by interacting with the coils located along the track. The arrangement maximizes the magnetic field on the track side while minimizing it on the opposite side, reducing magnetic exposure to passengers and using fewer magnets to achieve strong performance.
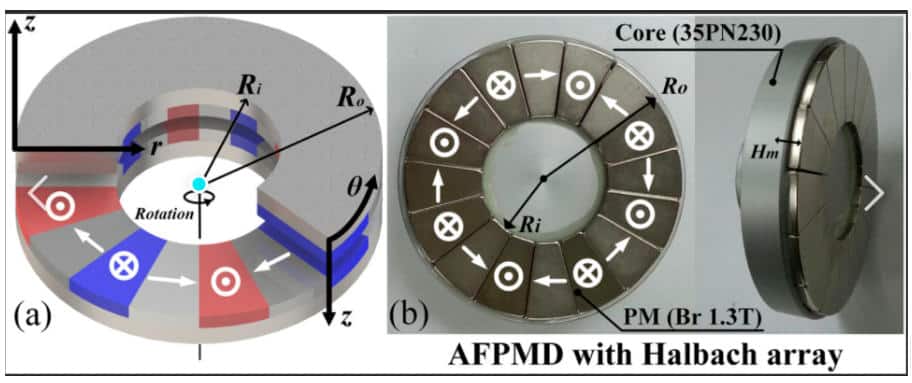
Ring (Annular) Halbach Array
The ring-type Halbach array can be regarded as a circular configuration formed by connecting the ends of a linear Halbach array, producing a continuous circumferential magnetic field.
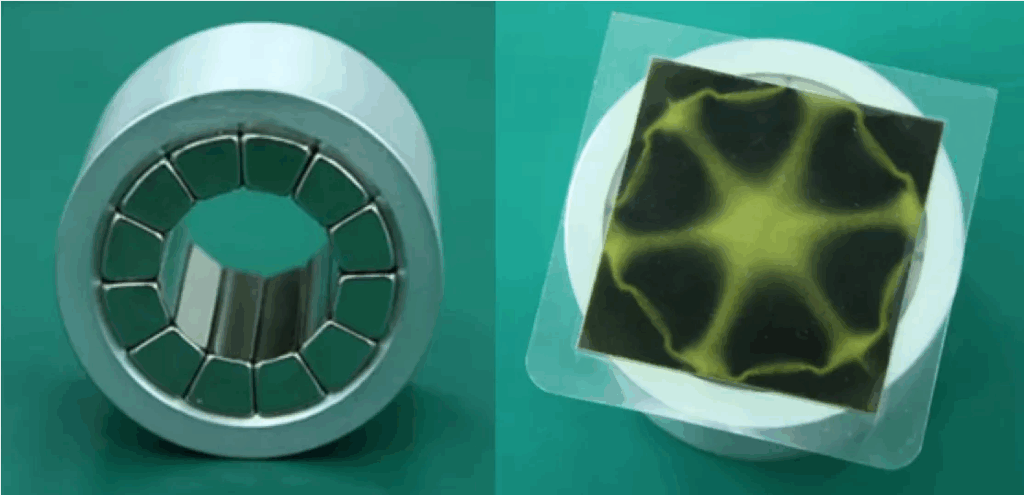
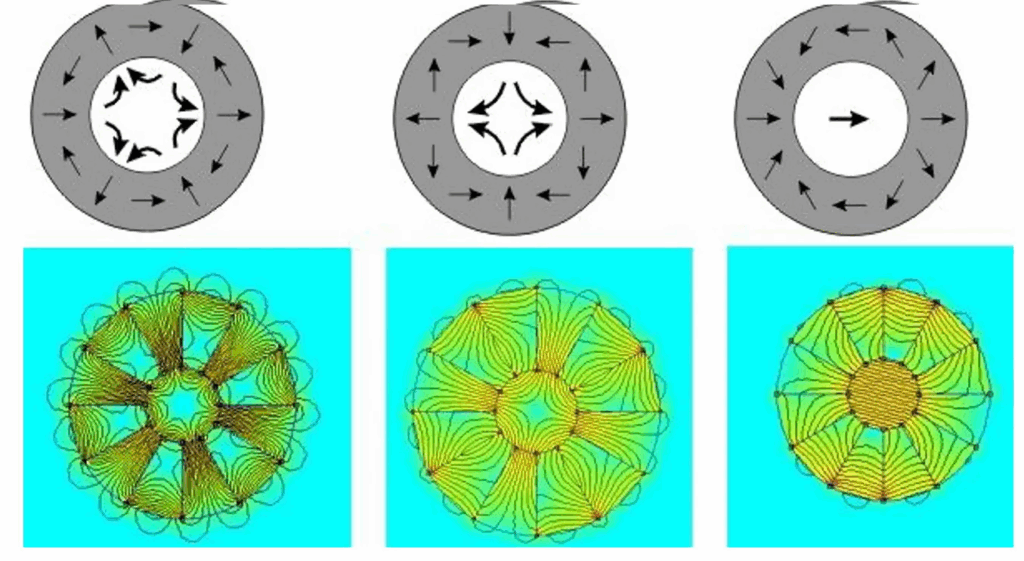
Halbach Array in Permanent Magnet Motors
In permanent magnet motors, the air-gap magnetic field of a Halbach array motor is closer to a sinusoidal distribution compared with that of a traditional permanent magnet motor. With the same amount of permanent magnet material, a Halbach array motor achieves higher air-gap magnetic flux density and lower iron losses.
In addition, Halbach ring arrays are widely used in permanent magnet bearings, magnetic refrigeration systems, and magnetic resonance equipment due to their efficient field distribution and unilateral magnetic properties.
Fabrication and Production of Halbach Arrays
Method 1: Segment Assembly
According to the topological structure of the array, pre-magnetized magnet segments are glued together. Because of the strong repulsive forces between segments, a mold or fixture must be used to hold them in place during assembly. While this method has low manufacturing efficiency, it is simple and easy to implement, making it suitable for laboratory research and prototyping.
Method 2: Integral Magnet with Post-Magnetization
A complete magnet is first formed by filling or pressing in a mold, and then magnetized in a specially designed fixture. The resulting array structure is similar to the illustration below. This method offers higher production efficiency and is well-suited for mass production. However, it requires careful design of the magnetization fixture and a well-defined magnetization process.
Method 3: Halbach type magnetic field distribution is realized by using winding array with specific shape, as shown below pic..