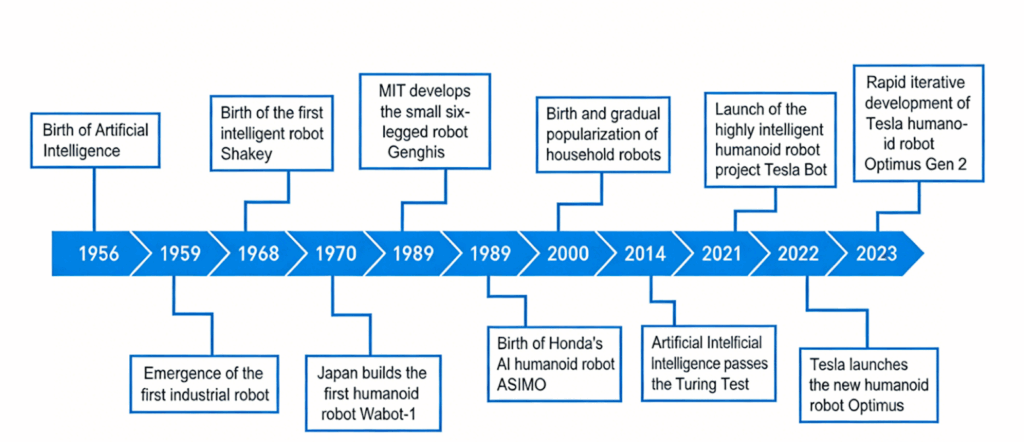
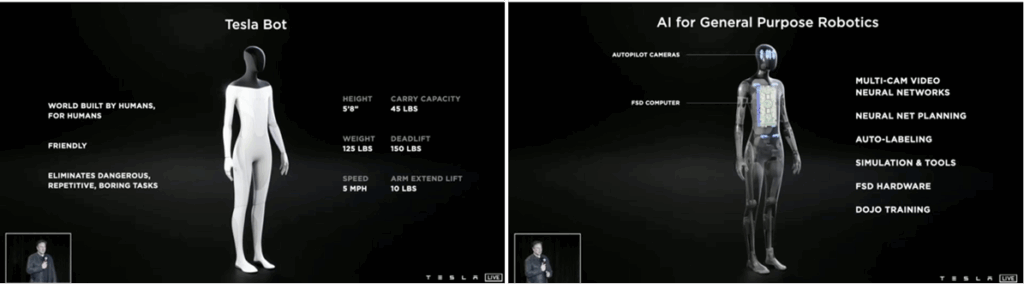
Humanoid Robots and Their Development History
Humanoid robots refer to robots with autonomy and first-person intelligence. Essentially, they are robots capable of perceiving and interacting with their environment, autonomously planning, making decisions, and taking actions, with actual execution capabilities.
The core goal of intelligent robots is to be able to understand human language, decompose tasks, plan sub-tasks, recognize objects while moving, interact with the environment, and ultimately complete the assigned tasks.
Structural Breakdown of Humanoid Robots
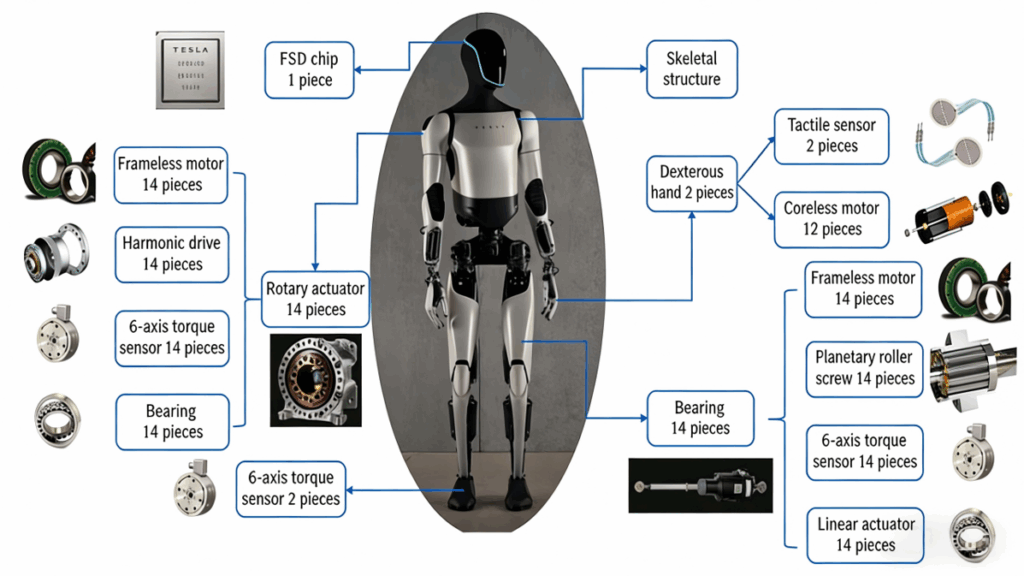
Application of Permanent Magnet Materials in Humanoid Robots (Frameless Motors)
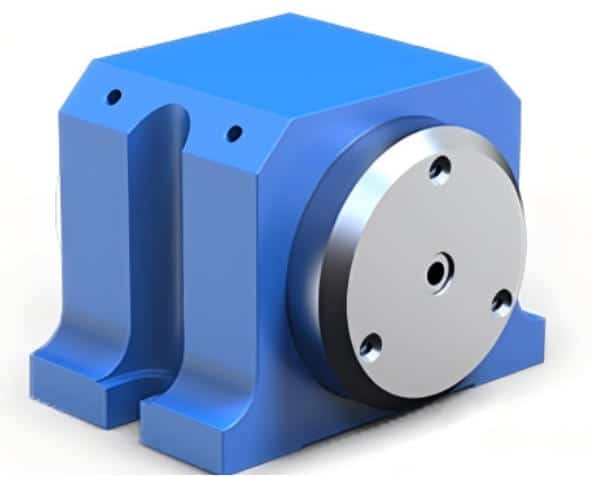
Frameless Motor: Power Source for Actuator Operation
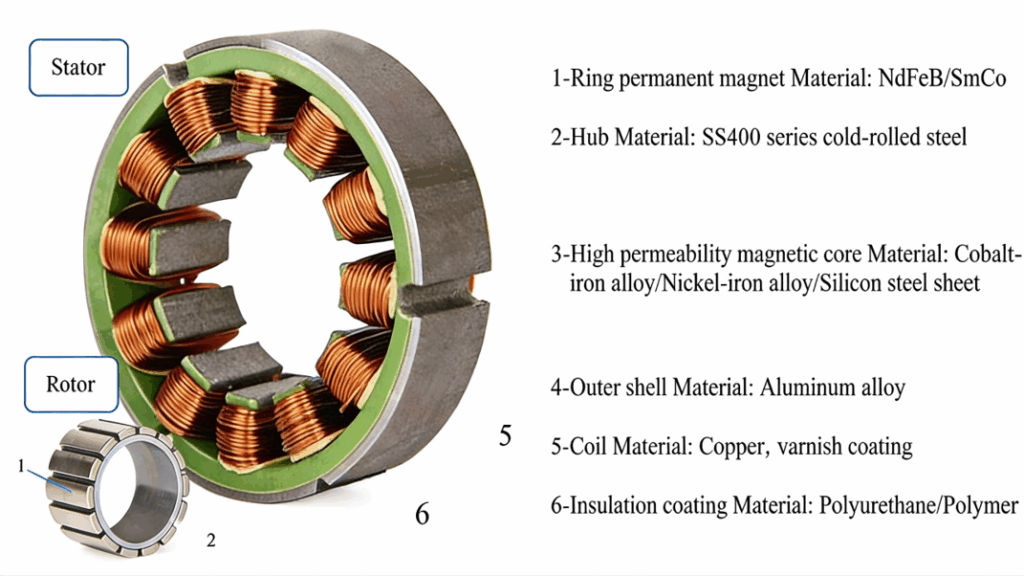
Frameless motors are the power source that drives humanoid robot actuators. They belong to a type of servo motor and are used to actuate the joints and motion systems of humanoid robots. By eliminating the traditional motor housing and shaft (and in some designs the iron core structure), frameless motors feature a compact and lightweight structure, enabling higher power density, as well as low energy consumption and low friction characteristics.
A frameless motor consists only of a stator and a rotor. The rotor is a rotating steel ring assembly equipped with permanent magnets and is mounted directly onto the machine shaft. The stator contains a high-permeability magnetic core surrounded by copper windings that generate electromagnetic force, and it is compactly integrated into the main body of the machine housing.
Application of Permanent Magnet Materials in Humanoid Robots (Coreless Motors)
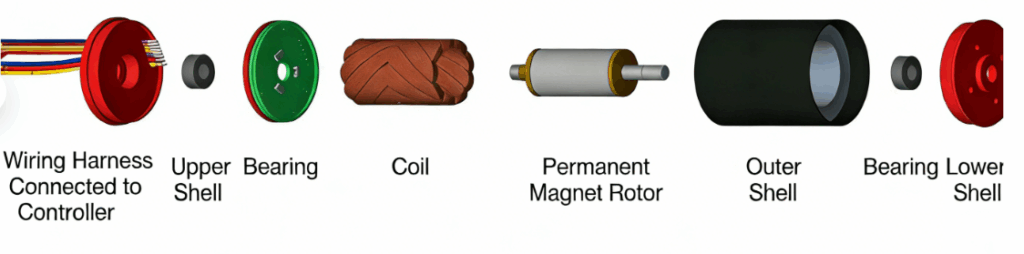
Coreless motors are DC permanent-magnet servo motors and belong to the category of micro special motors (with dimensions generally not exceeding 40 mm). Coreless motors feature small size, high efficiency, and low noise, and offer outstanding energy-saving performance, highly responsive and convenient control, and stable operation, demonstrating clear technological advantages.
For example, each dexterous hand of Tesla’s Optimus is equipped with six coreless-motor-driven joints, providing the hand with 11 degrees of freedom and enabling more flexible and precise manipulation.
The main components of a coreless motor include the coil, rotor, housing, and Hall sensors. The coil is wound with enameled wire, which consists of copper and insulating materials. The rotor is composed of permanent magnetic materials and an iron core, with the permanent magnet material accounting for the highest value among the components.

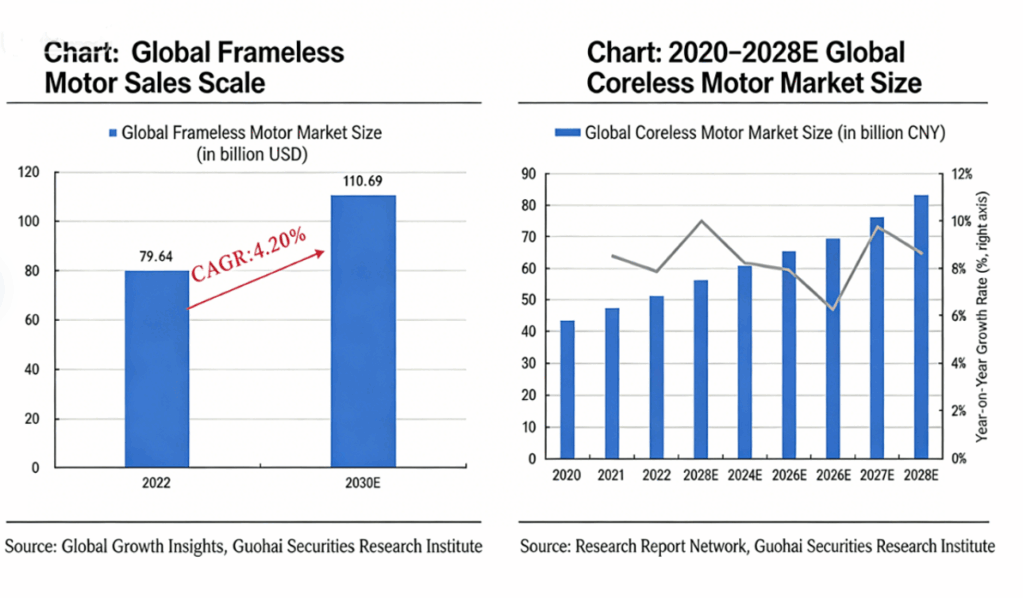
Global Market Size of Frameless Motors and Coreless (Hollow Cup) Motors
Robot joints require motors with small size, high torque, and fast response. Frameless torque motors are lightweight and high-power, and are able to deliver much higher torque at low speeds, making them well suited to the requirements of humanoid robots. Coreless motors feature compact size and excellent performance, making them particularly suitable for dexterous hands.